When dealing with large-scale ground power stations, complementary fishery and fishery, complementary agriculture and light-harvesting photovoltaic power plant procedures involving land acquisition and land lease, the first thing to look at is the nature of the land. After the inspection of the promising plots is completed, it is necessary to go to the local land bureau to inquire about the latest land use policy, the current status of the nature of the land, and the land use plan to determine whether it meets the requirements of policies and plans. First of all, it is necessary to clarify the classification of land properties, involving complementary projects of fisheries, light and light, and complementary projects of agriculture and the light, and in particular to clarify the relevant policies for agricultural land.
I. Land use planning classification system

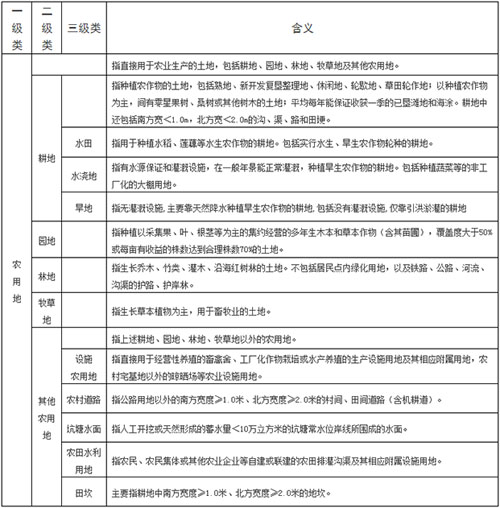
1. What is agricultural land?
According to the "Land Management Law" and the "Land Classification" promulgated by the Ministry of Land and Resources, agricultural land refers to land used for agricultural production, including cultivated land, garden land, forest land, pasture and other agricultural land. Agricultural land is divided into the following five types: cultivated land; garden; woodland; pasture; other agricultural land.
2. What is arable land?
According to regulations, cultivated land refers to the land for planting crops, including rehabilitated land, newly-developed and reclaimed land, recreational land, rotation land, and grassland rotation land; land that is mainly planted with crops, with sporadic fruit trees, mulberry trees, or other trees; On average, it is guaranteed that it will be harvested once a year for reclaimed beach and tidal flats. The arable land also includes ditch, canal, road and field ridge with a width less than one meter in the south and less than two meters in the north.
Arable land can be divided into three types:
1 Paddy fields refer to water source guarantees and irrigation facilities, which can be normally irrigated during the general years, and are used for cultivating aquatic crops, including irrigated paddy fields;
(2) The irrigated land refers to the arable land that can be normally irrigated except for paddy fields and vegetable fields where there are water source guarantees and irrigation facilities;
3 Dry land refers to cultivated land with no irrigation facilities and natural crops for growing dry crops, including cultivated land with no irrigation facilities and only flood irrigation;
3. What is the basic farmland?
Basic farmland refers to the cultivated land that cannot be occupied according to the demand for agricultural products according to population and socio-economic development in a certain period of time and based on the overall plan for land use. Corresponding to this is general agricultural land.
The basic farmland is part of the cultivated land, and it is mainly the part of the cultivated land with high yield and good quality. In general, the cultivated land allocated to basic farmland protection areas is basic farmland. The people said that the basic farmland was "eaten fields" and "safeguarding fields."

The scope of agricultural land is greater than that of cultivated land, and the cultivated land is greater than the basic farmland. Basic farmland refers only to arable land that is specially protected by the country.
Agricultural land can be converted into construction land through legal procedures. After the basic farmland has been determined according to law, no unit or individual may change or occupy it, unless it is the national energy, transportation, water conservancy, military installations and other key construction projects that cannot be avoided. Farmland conservation areas can only be occupied and must be approved by the State Council.
4. What is the conversion of agricultural land?
The conversion of agricultural land refers to the act of transforming agricultural land determined by land use status investigation into land for construction use after it is submitted for approval according to the overall plan for land use, the annual plan for land use, and the approval authority prescribed by the state.
Conversion of agricultural land to agricultural land is also referred to as construction land.
Second, photovoltaic power station and land use
In 2014, the National Energy Administration issued the “Notice on Further Implementing the Related Policies for Distributed Photovoltaic Generationâ€. The notification mentioned that "the use of abandoned land, barren hills, slopes, agricultural sheds, mudflats, fish ponds, lakes, etc. should be used for local consumption. Distributed photovoltaic power station."
The "flats, lakes, barren mountains and slopes" mentioned in the document are unutilized lands, and "fish ponds and agricultural greenhouses" belong to the category of agricultural land; abandoned lands may belong to construction lands, such as mining land.
To sum up, the state-owned resources of the land and the development of photovoltaic power stations must be aware of relevant land policies. In the early stages, the nature of land, land planning, construction planning, land ownership, land use, and ground attachments must be clearly implemented. Otherwise, once the project is launched. After the land problem occurs, it will cause huge losses.
Land use classification and meaning
Led Mirror,Led Hotel Mirror,Bathroom Light Mirror,Battery Led Light Mirror
Uni-Sec (Ningbo) Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hospitalityunisec.com