The main failure modes of the mold are surface wear, surface peeling, surface cracking, etc. Most of the failed molds can be repaired with appropriate maintenance techniques to restore their performance. At present, the repair technology of mold mainly includes thermal spraying, brush plating, surfacing welding, laser repair and other technologies. Professional mold repairing machines have appeared, and the wear-free parts of the mold are welded without heat, which can meet the requirements of wear resistance, heat resistance and corrosion resistance of the mold.
Due to the complicated manufacturing process of the mold, long production cycle and high processing cost, especially the manufacturing cost of precision complex molds or large molds is very high. For example, the cost of mold manufacturing and maintenance for FAW is as high as tens of millions of yuan per year. If the mold fails early, it will cause significant economic losses to the company. Therefore, the application of various repair techniques to repair the failed mold, and restore the use performance to put back into use, can achieve the purpose of extending the life of the mold, reducing costs, and improving economic efficiency.
The mold repair process is as follows.
(1) Process analysis and repair reasons → formulate repair plans and methods → repair → test and verification.
(2) Repair operation process Check the mold → Disassemble the damaged part → Clean the parts → Analyze, check, confirm the repair method → ​​Equipped and trim the damaged parts → Replace the repair parts → Assemble the mold → Try and verify.
First, thermal spray repair technology
Molds, especially hot work molds, not only work at higher temperatures, but also withstand wear, extrusion, impact and thermal fatigue. It is easily damaged during use, resulting in reduced service life. When the surface of the mold is worn or scratched, it can be repaired as long as the degree is not serious, thus extending the service life of the mold. The thermal spray repair technology mainly includes flame spraying, plasma arc spraying and supersonic spraying, etc., melting or softening a powdery or filamentous metal or non-metal material to form a droplet, and shooting at a certain speed on the surface of the pretreated substrate. Forming a metal with a certain bonding strength and a coating repairing mold of a compound such as WC or TiN can restore or even improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the mold.
1. Flame spraying and application
(1) Flame spraying Flame spraying is the use of gas (acetylene, propane, natural gas, etc.) and combustion-supporting gas (oxygen) mixed combustion as a heat source. The spray material enters the flame in a certain transmission mode, is heated to a molten or softened state, and then depends on the gas. Or the flame is accelerated to spray onto the substrate. Flame spraying is divided into wire flame spraying and powder flame spraying according to different spraying materials.
The flame spraying equipment is simple, easy to operate, and low in cost, but its coating layer strength is not high. The heat affected zone and the deformation are large, so it is often used for the repair of the surface shape of the low-strength mold, so that the service life of the mold is prolonged.
(2) Application Wuling Automobile Co., Ltd. used flame sprayed NiCr60A to repair the automobile beam forming die. Shaanxi Xianyang Deflection Coil Group Company used flame spray 30Cr13 to repair the imported coiled coil mold, and achieved good results.
2. Plasma arc spraying and application
(1) Plasma arc spraying plasma arc spraying is based on nitrogen (N 2 ), inert gas such as argon (A r ) as the working medium, ionization in a special spray gun to form hot plasma, and then enter the plasma arc zone. The powder coating material is melted, atomized, and sprayed at high speed onto the surface of the coated workpiece to form a coating.
The plasma arc spray heat source has high energy density and can be used for mold surface modification treatment or for surface repair of trace wear molds. However, the mechanical combination of the spray layer and the substrate is used for mold surface modification under non-impact load conditions. Sexual and shape repairs, such as plasma arc sprayed cobalt-based alloys on the surface of hot work dies, can last up to twice as long.
(2) Applying a 0.5~1.0mm alumina coating on a high melting point metal extrusion die made of tool steel, the operating temperature can be increased from 1320 °C to 1650 °C, sprayed with zirconia coating, extrusion temperature Up to 2370 ° C, the life of the mold can be extended by 5 to 10 times.
3. Supersonic spraying and application
(1) Supersonic spraying Supersonic spraying obtains a high bonding strength between the sprayed layer and the substrate, so it can be used for surface modification and repair of the mold under medium impact load, and the mold can be used without repair or reduction of machining after repair.
(2) Application of Guangzhou Nonferrous Metals Research Institute adopts supersonic spraying hard alloy technology to increase the repairing frequency of Cr12 steel deep drawing die from 500 pieces/time to 700 pieces/time, and the die life is increased by 3~8 times.
This technology has been successfully used by FAW Group to improve the surface modification of the important working surface of the drawing die, and the service life of the die is obviously improved.
Second, brush plating repair technology
Brush plating is a method of rapidly electrochemically depositing a metal or alloy coating on a local surface of a workpiece under normal temperature and no-groove conditions. Brush plating has the advantages of simple equipment, simple process, flexible operation, fast deposition speed, low surface roughness of coating, high hardness and corrosion resistance of coating. The brush plating method not only can improve the life of the mold by about 4 times, but also repair the worn mold, such as partial scratches on the surface of the mold cavity, pulling grooves, rust spot wear and other defects. After the repair, the wear resistance, hardness and surface roughness of the mold surface can reach the original performance index. At the same time, the cost of brush plating is low, generally accounting for only 0.5% to 2% of the cost of the mold.
The modern brush plating technology can complete the repair of the mold surface without disassembling the mold, and can ensure that the repaired working surface still has a sufficiently low surface roughness value.
The brush plating repair of the localized pulling groove of the CrWMn steel cavity mold is taken as an example for description.
Brush plating device
The brush plating device is shown in Figure 1.
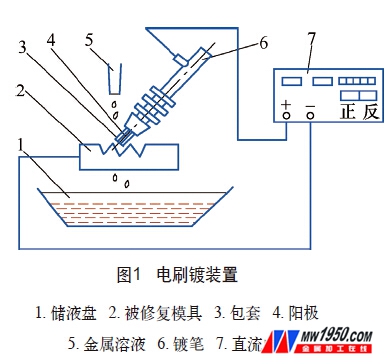
2. Power supply
It consists of a main circuit and a control circuit. The output of the main circuit is unidirectional 220V. After the AC power is stepped down and rectified, the 100H z pulsating DC power supply is output. The output voltage can be adjusted steplessly, usually 0~25V. The control circuit can control the thickness of the plating layer by the amount of electricity consumed.
3. Brush plating solution
(1) One of the pretreatment solutions, the electric cleaning solution. Used to eliminate oil stains on metal surfaces. Its formula is as follows: NaOH (CP) 35 ~ 50g / L, Na 2 CO 3 (CP) 40 ~ 45g / L, Na 3 PO 4 · 12H 2 O (CP) 140 ~ 180g / L, NaCl (CP) 4.4 ~ 5g/L. The solution has a pH of 12 to 13.
Second, the activation solution. There are two kinds of activation solutions A and B which can be used separately. The initial activation uses the A activation solution to completely expose the surface lattice of the metal. The B activation solution is used again to eliminate the black-gray carbide and make the substrate silver-white. A activation solution formulation: H 2 SO 4 (CP) 80~85g/L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 110~120g/L. The solution has a pH <2. B activation solution formulation: Na 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 )·2H 2 O (CP) 142~145g/L, H 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 )(CP) 90~100g/L, NiCL 2 · 5H 2 O(CP) 2~5g/L. The solution had a pH of 4. In the formula, CP represents chemically pure, Na 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 )·2H 2 O is sodium citrate, and H 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 ) is citric acid.
(2) One of the metal solutions, a special nickel solution. The solution can improve the platability of the metal substrate and improve the bonding strength between the substrate and the working layer, generally 1 to 3 μm. The formulation is as follows: NiSO 4 ·6H 2 O380~400g/L, NiCl 2 ·5H 2 O14~20g/L, H 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 ) 30~70g/L, HCl20~40g/L. The solution pH = 1.
Second, a fast nickel solution. The solution deposits metal at a high speed, the hardness after repairing the mold is about 52HRC, has good wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and has good bonding force with the CrWMn steel mold base. The formula is as follows: NiSO 4 ·6H 2 O250~300g/L, K 3 (C 6 H 5 O 7 ) 80~130g/L, buffer salt A40~60g/L, buffer salt B20~30g/L, additive 0.1g /L. The solution has a pH of 7-8.
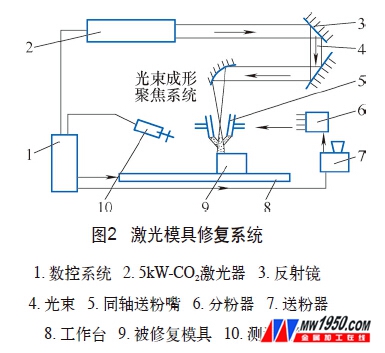
4. Operation process
Surface pretreatment (the fitter repairs the groove surface of the mold to facilitate the contact of the plated pen with the groove; after the repaired part is modified, the surface roughness Ra is 6.3 μm or less; the thickness of the metal to be repaired is measured, and the insulating paint is used. Or polyester tape to protect the non-repair area)→Electric net (the mold is connected to the negative electrode, the plate is connected to the positive electrode, the oil is cleaned to remove the oil on the repair surface, the voltage is 10~20V, the time is 10~30s)→The tap water is washed→activated (using A activation Liquid, voltage 6~12V, time 5~30s, surface is dark gray)→ tap water rinse→activation (using B activation solution, voltage 15~25V, time 5~30s, surface is silvery white)→ primer layer (select special nickel) Solution, voltage 8~12V, relative wiping speed 15mm/min, plating thickness 1~3μm)→ tap water rinse→plating working layer (select fast nickel solution, voltage 8~15V, relative wiping speed 15mm/min)→ tap water rinse → Trimmer trimming (to achieve the desired shape and size).
Third, laser cladding repair technology
Laser cladding is the use of a high-energy laser beam to irradiate the metal surface to melt the coating material, bond with the substrate and solidify rapidly, forming a layer of material with special physical, chemical or mechanical properties on the surface of the substrate. Laser cladding technology can now not only surface repair the forming mold, but also surface modification of the formed mold. The characteristics of laser cladding are as follows: 1 laser heating and cooling are fast, and the cladding layer is fine and dense. 2 The energy density of the laser beam is high, the laser cladding has little heat influence on the substrate, and the deformation is small, and the mechanical properties of the substrate are not damaged. 3 can effectively modify the local area or repair cracks, chipping and wear sealing edges. 4 The power, position and shape of the laser beam can be precisely controlled, and it is easy to realize precise repair of the selected area and even the micro-area cladding, and realize different mechanical properties in different parts of the mold with a small cost. 5 The requirements for matrix materials are low, and this technology can be applied to most materials. 6 can achieve large area and deep thickness repair.
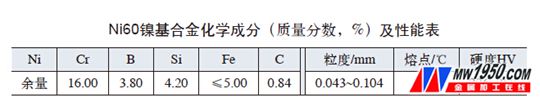
1. Common cladding materials
At present, the materials commonly used in laser cladding mainly include self-fluxing alloy materials, carbide dispersion or composite materials.
2. The choice of laser
At present, CO 2 lasers are used more and are more effective. The lasers have high power and uniform energy distribution, and are particularly suitable for large-area cladding.
3. Laser cladding process
Laser cladding can be roughly divided into two categories according to the supply mode of the cladding material, namely preset laser cladding and synchronous laser cladding. Pre-set laser cladding is to pre-position the cladding material on the surface of the substrate and then scan and melt it by laser beam irradiation. Synchronous laser cladding is to directly place the cladding material into the laser beam. In order to complete the feeding and cladding simultaneously, the cladding material is added in the form of powder, silk and plate, and the powder is most commonly used and relatively mature.
(1) Main process flow of preset laser cladding: pretreatment of substrate cladding part → preset → cladding treatment → preheating → laser melting → post heat treatment.
(2) Main process of synchronous laser cladding: pretreatment of substrate cladding part→feeding→laser melting→post heat treatment.
4. Application
Volkswagen Santana car trunk beam deep drawing die surface laser repair. Repairing parts: arc angle at both ends of the mold; base material: ductile iron; performance requirements after repair: wear resistance, hardness 50~55HRC; repair thickness about 3mm.
The laser repair of the 5CrMnMo steel mold is described below as an example.
(1) Laser repair system Laser repair technology is a collection of high-power laser, computer, CNC machine tools, CAD / CAM, advanced materials, CNC technology and other scientific applications. The laser repair process is shown in Figure 2. First, a coaxial powder feeding device. The powder feeding device is composed of a powder feeder and a coaxial powder feeding nozzle. In the lower part of the powder hopper of the powder feeder, gas-solid two-phase fluidization is formed due to the action of the equilibrium air pressure, and the pores are opened from the conduit to transport the powder with the carrier gas. The powder feeding amount is adjusted by the pressure of the conveying gas, and the powder feeding range is widened, and the powder is uniformly and continuously fed from 5 to 150 g/min, and the powder feeding precision is up to ±5%.
Second, the control of the mold repair process. Infrared temperature measurement technology is used to detect the temperature field of the laser processing area, and the actual temperature field information is derived by combining the temperature field calibration results to control the laser power output value and the movement speed of the CNC machine tool to keep the temperature of the molten pool stable and avoid the mold due to Overheating or uneven temperature causes defects such as cracks and pores. The colorimetric thermometer is used for temperature measurement, and the optical path system uses a single camera to switch the single-channel image recording mode of different color filters. The filter and its control ensure that the two filters are alternately placed in the digital camera image recording optical path, and the moving response time is <10ms. The computer-controlled high-precision stepping motor realizes accurate positioning.
(2) Laser repair mold process parameters Laser repair process parameters are mainly laser power P, scanning speed vs, powder feeding speed vf, molten pool temperature and so on. In the laser repair process, it is necessary to control the melting point of the molten material (take the highest melting point of both the matrix and the powder material) Tm+(50~100) °C. Reference temperature field calculations, the theoretical value of P takes 1 ~ 2kW, v s is 2 ~ 4mm / s meet the requirements. As for the surface roughness of the cladding layer, it can be minimized by adjusting the amount of powder fed.
(3) The laser repair equipment adopts a cross-flow continuous wave 5kW-CO 2 laser, the light speed mode is multimode, the spot diameter is 4mm, and the base material (mold) is 5CrMnMo steel. Since the Ni alloy powder has good fluidity and the surface is smooth and the price is moderate, the Ni60 nickel-based alloy powder material is selected, and its chemical composition is shown in the attached table. The selected laser power P was 1.5 kW, v s = 3.2 mm/s, and v f = 310 mg/s.
(4) Process In the process of laser repairing mold, the process parameters P=1.5kW, V s =3.2mm/s, V f =310mg/s, and the thickness of the cladding layer is 1~2mm, which can obtain ideal surface quality. In order to prevent cracks on the surface of the mold, the mold may be subjected to a preheat treatment at 200 ° C × 2 h. The laser cladding portion can be protected by argon side blowing during the repair process. Actually used for mold repair requires the control part of the laser repair system to continuously adjust the powder feeding speed v f to overcome the unevenness of the surface of the cladding layer.
(5) Test results After the laser cladding layer structure is examined, a repair layer having uniform structure, fine density and excellent performance can be obtained in a relatively wide range. The quality of mold repair can be improved by optimizing the process parameters and the method of preheating the substrate.
Fourth, surfacing technology and application
The principle of surfacing technology is to weld the filler metal to the surface where the mold is damaged to obtain the required performance and specifications. Surfacing welding of the mold can greatly reduce the cost and shorten the production cycle, so the surfacing technology has been widely used. Divided into arc surfacing and spark surfacing according to the process. Stress relief annealing is usually performed after surfacing to prevent cracking.
Due to the need of market competition, the trial production cycle requirements of new products are very short, and the old molds that have been used for mass production are often replaced by prototypes instead of trial molds. Sometimes the shape of the product is changed during the trial production process, and the mold needs to be trimmed. The dressing of the mold usually requires that the materials used have good weldability. Precipitation hardened steel can generally be surfacing. The machining, mirror finishing and patterning properties of the surfacing are the same as those of the substrate.
After the hot forging die is worn or deformed to affect the dimensional accuracy after a period of use, it can be repaired or machined to renovate the mold.
1. Local surfacing repair of crankshaft forging die
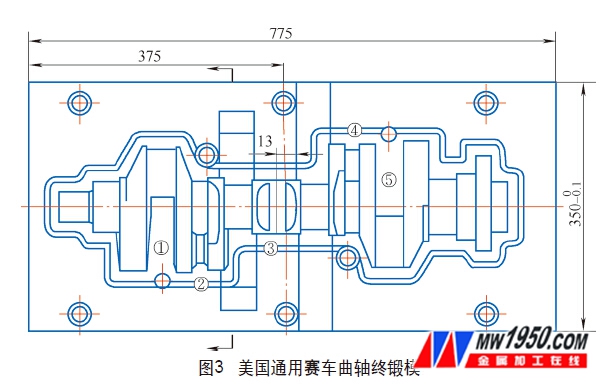
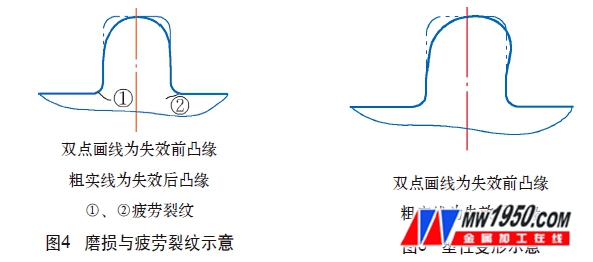
(1) Repair parts of the mold The most common failure mode of the crank forging die is the wear of the flange part of the mold (see Figure 3, 1~5) (see Figure 4), fatigue crack (see Figure 4), crack, brittle fracture And cracking, plastic deformation (see Figure 5). Wear, deformation, cracking, and fracture of the flange portion mean the end of the overall mold life. In order to improve the service life of the mold, local over-welding of the mold can be carried out, that is, the local fatigue crack, wear and plastic deformation are repaired by surfacing technology.
(2) 45Cr2NiMoVSi steel for medium and small hammer forging die and 5CrNiMo steel for large hammer forging die.
(3) Mold repair process First, the mold is preheated as a whole, and then the relevant parts are surfacing. For the crack cracking and cracking parts, the cracks should be cleaned, and then the surfacing welding should be carried out with the mold steel electrode, and finally the furnace is aged to eliminate the stress. If the preheating, surfacing and aging processes are reasonable, the life of the surfacing site is basically the same as or higher than that of the substrate.
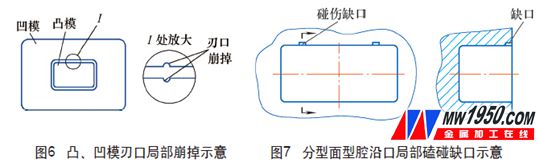
2. Localized chamfering repair of the convex and concave die edge
When there is a partial collapse of the edge of the punch and the die (see Figure 6), the collapsed part can be repaired by the same electrode as the base material of the convex and concave molds, and the dimensional accuracy of the pattern is required after surfacing. Processing, but processing should be performed after the surface is annealed.
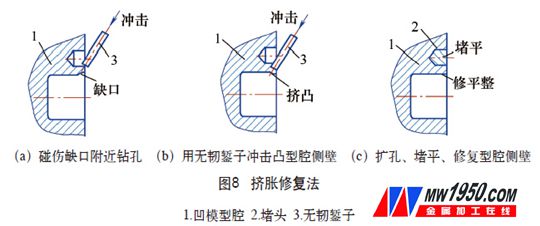
3. Plastic mold cavity repair along the mouth
The plastic mold parting cavity is bumped along the mouth to produce the notch shown in Fig. 7. The repair methods include the repair welding repair method and the squeeze repair method (see Fig. 8). The repair welding is performed by argon arc welding, and the repair is completed by the fitter. The diameter of the drill hole near the notch is generally 8~10mm, and the side wall of the extruded cavity is trimmed by the fitter, and the plug and the parting surface should be flattened.
4.40Cr steel mold surfacing repair
(1) Clean the surface of the mold, CO 2 gas shielded welding, wire grade H08Mn2SiA, diameter 0.8mm, welding current 100A, arc voltage 18~21V, short circuit transition, firstly rotate the mold parts to ignite at the climbing position The arc is welded to advance the weld bead in a spiral manner to achieve uniform heating of the weld bead in one week and prevent deformation and bending of the mold part. (2) The surface temperature of the mold parts is controlled at 200 ° C, and the temperature is kept for 2 hours after welding, and air cooling is performed.
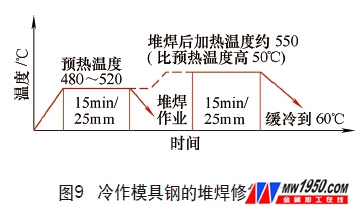
5. Surfacing repair of hardened die steel mold
The surfacing performance of hardened die steel is much worse than that of flame hardened steel, so cracking is more likely to occur during surfacing. The crack is mainly caused by the fact that the cooling rate after welding is too fast. A tempering furnace must be provided for welding, and the mold to be welded is preheated in advance (480 to 520 ° C), then quickly welded and repaired, and then placed in a tempering furnace at a temperature 50 ° C higher than the preheating temperature. After the welded parts placed in the furnace reach the holding time, they are cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The repair process of the mold is shown in Figure 9. At the same time, the electrode should be selected to suit the material of the mold to be welded. In the welding operation, for the sake of simplicity, a common gas welding torch is used to heat the mold to a certain preheating temperature, but since this method is easy to cause a large or complicated mold to crack during the preheating process, in general, This method is not allowed for preheating. Gas welding torch preheating and surfacing repair can only be used after the mold has been annealed or tempered at high temperature.
The above procedures can be summarized as follows:
Broken mold → annealing or high temperature tempering → preheating before welding (480~520 °C) → heating after rapid welding repair (550~580 °C) and cooling with furnace → repair finishing → (heat treatment) → grinding or grinding → finished product .
Five, mold repair machine repair
The mold repairing machine is a high-tech equipment for repairing surface wear and processing defects of the mold. The mold repairing machine strengthens the long life of the mold and has good economic benefits. Various metal-based alloys such as iron-based alloys (carbon steel, alloy steel, cast iron) and nickel-based alloys can be used for surface strengthening and repair of various metal molds and workpieces, and the service life is greatly improved.
1. The principle of the mold repair machine
It uses the principle of high-frequency electric spark discharge to repair the surface defects and wear of the metal mold without hot surfacing. The main feature is that the heat affected area is small, the mold will not be deformed after repair, no annealing, no stress concentration, no Cracks appear to ensure the integrity of the mold; it can also be used to strengthen the surface of the mold workpiece to meet the performance requirements of the wear resistance, heat resistance and corrosion resistance of the mold.
2. Application range
Mold repairing machine can be used in machinery, automotive, light industry, home appliance, petroleum, chemical and electric power industries, for repairing and surface strengthening of hot extrusion die, hot extrusion die, hot forging, roll and key parts. .
For example, ESD-05 type EDM welding repair machine can be used for injection mold repair of wear, bruises and scratches, as well as rust, peeling and damage repair of die-casting molds such as zinc-aluminum die-casting molds. Machine power 900W, input voltage AC220V, frequency 50~500Hz, voltage range 20~100V, output percentage 10%~100%.
Sixth, other repair techniques
1. Using heat treatment shrinkage process to repair worn cold work die
(1) After the cold heading model cavity is worn, it can be repaired by shrinkage hole treatment and re-quenching, and reinstalled. The shrinkage hole heat treatment process can heat the mold to 600~650 °C, and then the mold is cooled from the outer surface to the center. When cooled to about 150 °C, the outer surface of the mold shrinks, so that the mold center can generate compressive stress and make the type The cavity shrinks 0.15~0.20mm. The shrinkn mold can be reused after re-quenching. Generally, under normal conditions, this method can be processed 2 to 3 times, which can greatly extend the total life of the mold.
(2) T10, T11 steel drawing and deep drawing die, after wear and tear in the work, it can be heated by high temperature first, then re-normally quenched, and can be repaired by shrinkage hole.
2. Blanking die convex and concave die repairing method
(1) Grinding repair method When the cutting edge of the punching die is less than 2 mm, the grinding method is generally used to remove the chipping position to achieve the repairing purpose. When using this repair method, due to the large grinding allowance, the cutting fluid should be used for cooling to prevent annealing during grinding.
(2) Blade inversion repair method When the edge of the convex and concave die block has a chipping depth of more than 2 mm and it is not suitable to be repaired by grinding, the blade can be removed and turned over and reassembled to achieve the purpose of repair. When adopting this method, the convex and concave mold blocks must be symmetrical, and the shape of the upper and lower shapes should be completely uniform, and the screw hole is a through hole. In order to ensure the quality of the repair, the cylindrical pin hole on the panel must be enlarged by about 5 mm. After the pin plug is flattened, the fixed block is used as a pin hole.
(3) Adding block repairing method Some convex and concave mold blocks can not be repaired by inversion method. EDM and wire cutting methods can be used to cut the chipping part in the height direction, and then reassemble after adding the pad below. Reach the repair requirements. When repairing, the outer dimensions of the block can be made according to the block, which is generally slightly smaller than the size of the block 0.1~0.2mm, and the thickness of the block is slightly larger than the thickness of the cut. Generally, the thickness is increased by 0.3~0.5mm, so that it is fixed after assembly. Grinding allowance.
(4) When the depth of the chipping in the repairing method is greater than 10mm or the blade surface has cracks in the thickness direction, it can be repaired by the inserting method. Since the crack cannot be repaired by the inversion method or the pad method, the line is used. The cutting method removes the defective part and then inserts a blade of the same size to repair it. In order to ensure sufficient strength after the blade is repaired, the size of the die-and-concave die block using this repair method cannot be too small. The matching method generally adopts no-gap fit. In order to prevent the block from being cracked after being inserted, there should be no overfill when inserting. If there is a gap, it can be adhered with an adhesive. The shape of the mating portion generally has two shapes of a circle and a dovetail shape. The insert should be oiled before it is inserted, and then gently pressed in. The material of the insert can utilize the blade of other scrap molds.
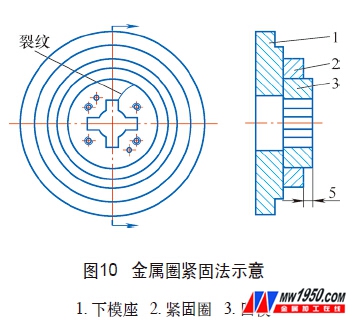
(5) Metal ring fastening repair method When the integral die is cracked, it can be fastened to the original size with a metal ring on the outer surface. This method can also be used when some of the smaller combined die blocks are loose. The material for fastening the metal ring can be made of Q235A steel, and the thickness is about 5mm below the die. In order to facilitate the processing and assembly, the metal ring and the concave die can be matched with a clearance of about 0.1 mm. After the metal ring is inserted into the die, the metal ring is fixed to the die base by screws, and the surrounding joints are fastened with a flat boring to restore the die to the required size. . Figure 10 is a schematic illustration of the metal ring fastening method.
About the author: Jin Rongzhi, vice president of Harbin Huilong Auto Box Bridge Co., Ltd.
Fountain Nozzles, wholesale nozzles, fountain parts
Wuxi Jinshanghua Environmental Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.jshfountain.com