0 Preface
The pressure oil tank belongs to the second type pressure vessel. According to the different amount of water, it controls the angle of the turbine generator blade in the hydropower station. The design working pressure is 6.3MPa, the hydraulic pressure test pressure is 8.75MPa, the design working temperature is 50°C, and the working medium is oil. The seam coefficient is 1, the volume is 19.78m3, the cylinder and the head are made of 16MnR normalized state material, and the steel plate is ultrasonically flawed one by one. The quality is in accordance with the standard JB4730-94 grade III, and the A and B butt welds are 100% γ. Radiographic inspection, qualified according to JB4730-94 standard II. After passing the test, ultrasonic testing is carried out at 20% of each welding length. According to JB4730-94 standard I grade, manhole, flange and take-over are all in accordance with JB4726-2000. Standard 16MnIII grade forgings (normalized), D-type joints shall be tested for 100% magnetic particle after welding, and qualified according to JB4730-94 standard I. After all the equipment has been welded and the non-destructive testing is passed, the overall stress relief heat treatment is carried out. During the hydrostatic test, cracks were generated at the joint weld between the manhole joint forging and the cylinder. During the subsequent crack repair, it was found that during the carbon arc gouging process, the crack was continuously expanded from the weld to the forging, the forging carbon After the arc gouging blows off about 600mm long and 20mm deep, cracks continue to be generated. In some parts, no cracks were found at the time, but then cracks were generated and the welding was stopped. In order to analyze the causes of this phenomenon, from the manhole nozzle forgings where the cracks have been scrapped during the repair, samples are taken for chemical composition analysis, mechanical property test, macroscopic microscopic metallographic observation to find out the cause of the problem and formulate treatment measures. .
1 Test materials and methods
1.1 Test materials
The barrel material is 16MnR, the plate thickness is 50mm; the manhole nozzle is 16Mn forging (JB4726-2000 standard grade III), its size is φ572/φ450×425 mm, the nominal chemical composition of 16MnR barrel material and the chemical provided by the supplier The composition, the nominal of 16Mn forgings and the chemical composition and measured chemical composition provided by the supplier are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical composition of tube sections and forgings (Wt%) 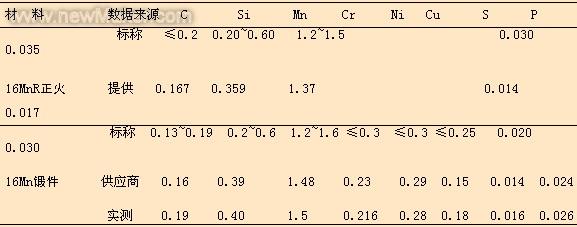
Tensile specimens, impact specimens and metallographic specimens were respectively cut from the scrapped manhole forgings according to the tangential direction. The standard Charpy impact specimens were prepared according to the GB/T229 standard by machining method, respectively, at room temperature. 0 °C impact test, and direct observation of the impact fracture; tensile specimens prepared according to R4 (d0=10mm, l0=50mm) in GB/T6397, tensile test according to GB/T228 standard; metallographic test The sample was ground to 1800# on metallographic sandpaper, then polished on a P-2 type polishing machine with an aqueous solution of chromium trioxide, washed and then etched with hot acid to reveal the microstructure of the sample. Observation of the impact fracture and metallographic specimens was performed in a Quanta 400 scanning electron microscope (SEM). The chemical composition analysis was carried out by a dissolution method.
2 test results and analysis
2.1 scrap hole forging forgings
2.1.1 Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of forgings are listed in Table 2. The evaluation criteria are according to JT4726-2000 [1] for carbon steel and low alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels. It can be seen from Table 2 that the mechanical properties of the measured forgings are different from those provided by the supplier. Large, its strength exceeds the standard upper limit, the impact energy is far below the minimum required by the standard, showing high strength, low enthalpy, low toughness.
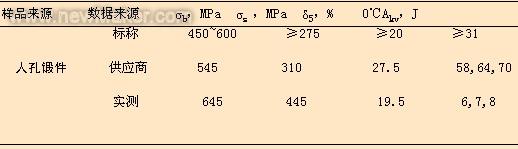
Table 2 Mechanical properties of scrapped forgings
After the carbon arc gouging of the forging, a macroscopic visible crack originates from the groove of the carbon arc gouging. The crack is about 12 mm long and is expanded by the welded yoke to the forging, as shown in Fig. 1a. The dark gray area near the groove under the metallographic microscope is shown as a white bright area under the scanning electron microscope. See Fig. 1b, the dark gray area near the groove is martensite + retained austenite, hardness HV0.1 500, 454, 438; The hardness of the adjacent region with dark gray is HV0.1331311,323, and its microstructure is (Fig. 1C) troostite→sauersite→somsite+ferrite→irregular massive ferrite+pearlite. The tissue away from the crack is irregular massive ferrite + pearlite, see Figure 1d. The polished surface of the sample was observed, and there was no decarburization near the crack, and there was no serious inclusion. It has been determined that the grain size of the manhole forgings is 4 to 5, which is relatively large, as shown in Fig. 1d.


(a) macroscopic metallography; (b) characteristics of crack initiation sites;


(c) away from the cracked area; (d) deep gray area of ​​the grooveFig. 1 crack and microstructure of the manhole joint forging

Figure 2 Impact fracture morphology of manhole forgings
2.2 Mechanical properties and metallographic structure of the forged manhole forgings
The forged parts were replaced by scrapped forgings and the forgings were reused by reheating. The scraped manhole pipe forgings are regarded as the furnace heat treatment test plates, and the unqualified manhole pipe forgings are subjected to normalizing at 900 ° C to 930 ° C and tempering at 600 ° C to 620 ° C for heat treatment [4]. The tensile, tensile and metallographic samples were taken from the tangential direction on the plate. The mechanical properties are listed in Table 3. Compared with the data in Table 2, the mechanical properties of the 16Mn manhole forgings are obviously improved. Meet the standard requirements; the metallurgical structure of the base material after fire and tempering is ferrite + pearlite, the grain size is 9.5 ~ 10.5 grade, as shown in Figure 3, the grain is obviously refined. Obviously, the reheated structure of high temperature forging is restored by re-heat treatment, the metallographic structure is improved, the crystal grains are refined, the academic performance index meeting the standard requirements is obtained, and the use requirements are met, and the manhole joint forgings are renormalized by tempering and tempering. It can be reused after heat treatment.
Table 3 Mechanical properties of recycled forgings 

Figure 3 Manhole tube forgings after normalizing the tissue × 100
The manhole joint forgings are reheated by normalizing and tempering, and then welded to the cylinder. Because the welding of the forgings and the barrel of the manhole is used, the embedded T-type fully-dissolved welded joints extending at both ends are used, and the structural rigidity is adopted. Larger, welding restraint stress [5], must preheat before welding 100 ° C ~ 150 ° C, the interlayer temperature is not lower than 150 ° C, after the inner wall is welded, the intermediate dehydrogenation treatment to compensate for the lack of interlayer temperature, After the outer wall is welded, the final hydrogen-removing treatment is carried out. The welded joint of the forged joint of the mandrel and the cylinder as above is welded, and after 24 hours, according to the JB4730-94 ultrasonic flaw detection class II standard, once qualified.
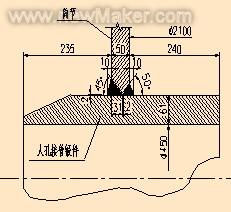
Figure 4 Manhole joint forgings and barrel joint welding
1) Since the forging of the tubular manhole pipe forgings is not strictly normalized according to the requirements, the overheated structure of the manhole pipe forgings is not restored, and the crystal grains are coarse, resulting in the joint weld of the manhole pipe forgings and the cylinder body under the high restraint of the thick plate. Cracks occur during welding.
2) The forgings are reheated by normalizing and tempering, which can completely improve the metallographic structure, refine the grains, obtain the mechanical properties required by the standard, and meet the requirements for use.
3) The combined weld of the forging and forging of the manhole joint after reheating, using the welding process of the hydrogen elimination treatment after preheating welding before welding, no crack is generated under the high restraint welding of the thick plate, and the weld flaw detection is qualified once. .
High-performance microcentrifuge tubes, optimized design, and high-performance quality help protect your samples. Microcentrifuge tubes are made of polypropylene (PP) and are highly mechanically stable, ensuring your samples are stored, run and centrifuged worry-free.
Microcentrifuge tubes have a maximum centrifugation tolerance of 25,000 x g and are autoclavable (20 minutes, 121°C). The centrifuge tube adopts a snap-on tube cover design, which can be operated with one hand and has good sealing performance, which can effectively prevent liquid leakage; the tube wall is smooth, and the tube body is designed with a frosted area for convenient marking.
microcentrifuge tube sizes,microcentrifuge tubes 1.5 ml,microcentrifuge tubes uses
Yong Yue Medical Technology(Kunshan) Co.,Ltd , https://www.yonyuemedicals.com