Coaxiality detection is a problem we often encounter in measurement work. The use of three-coordinate for coaxiality detection is not only intuitive and convenient, but also has high accuracy and good repeatability. There are many products in auto parts manufacturing enterprises that require strict coaxiality inspection, especially the inspection of export products, such as EATON differential housing, AAM fork, and main reducer housing. Therefore, it is possible to accurately measure the coaxiality of such parts to have a certain influence on the subsequent assembly.
1. Factors Affecting Concentricity The definition of the coaxiality tolerance zone in the national standard refers to the area within the cylindrical surface whose diameter tolerance is the value t and which is coaxial with the reference axis. It has the following three control elements: 1 axis and axis; 2 axis and common axis; 3 center and center.
Therefore, the main factors affecting the coaxiality are the center position and the axial direction of the measured element and the reference element, especially the axial direction. For example, measure two cross-section circles on the reference cylinder and use the connection as the reference axis. Two cross-section circles are also measured on the cylinder to be measured, a straight line is constructed, and the concentricity is calculated. Assume that the distance between the two sections on the reference is 10 mm, and the distance between the first section of the reference and the first section of the cylinder to be measured is 100 mm. If the center position of the second section circle of the reference is 5 μm from the center of the first section circle, The error, then the reference axis has deviated from the first section of the cylinder to be measured by 50μm (5μmx100÷10). At this time, even if the cylinder to be measured is completely coaxial with the reference, the result will be 100μm (coaxiality tolerance). The value is the diameter, 50 μm is the radius), and the measurement principle is shown in Figure 1.
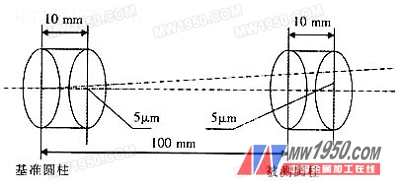
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of coaxiality measurement
2. The method of measuring the coaxiality by three coordinates can not be directly obtained by the measurement software when the reference cylinder is far away from the cylinder to be tested (short), and is usually obtained by the common axis method, the straightness method and the distance method.
2.1 The common axis method measures the circle of multiple cross-sections on the measured element and the reference element, and constructs a 3D line of the center of these circles as a common axis. The diameter of each circle can be inconsistent, and then calculate the reference cylinder and the Measure the coaxiality of the cylinder to the common axis and take the maximum value as the coaxiality of the part. This common axis approximates a simulated mandrel, so this approach is close to the actual assembly process of the part.
Next page
Thin wall ball bearings are simple in structure and easy to use. Mainly used to bear radial load, but when the radial clearance of the bearing is increased, it has a certain performance of Angular Contact Ball Bearing and can bear combined radial and axial load.
When the speed is high and thrust ball bearings are not suitable, thin wall ball bearings can also be used to bear pure axial loads. Compared with other types of bearings of the same size, this type of bearing has a small friction coefficient and a high limit speed. But it is not impact resistant and not suitable for heavy loads.
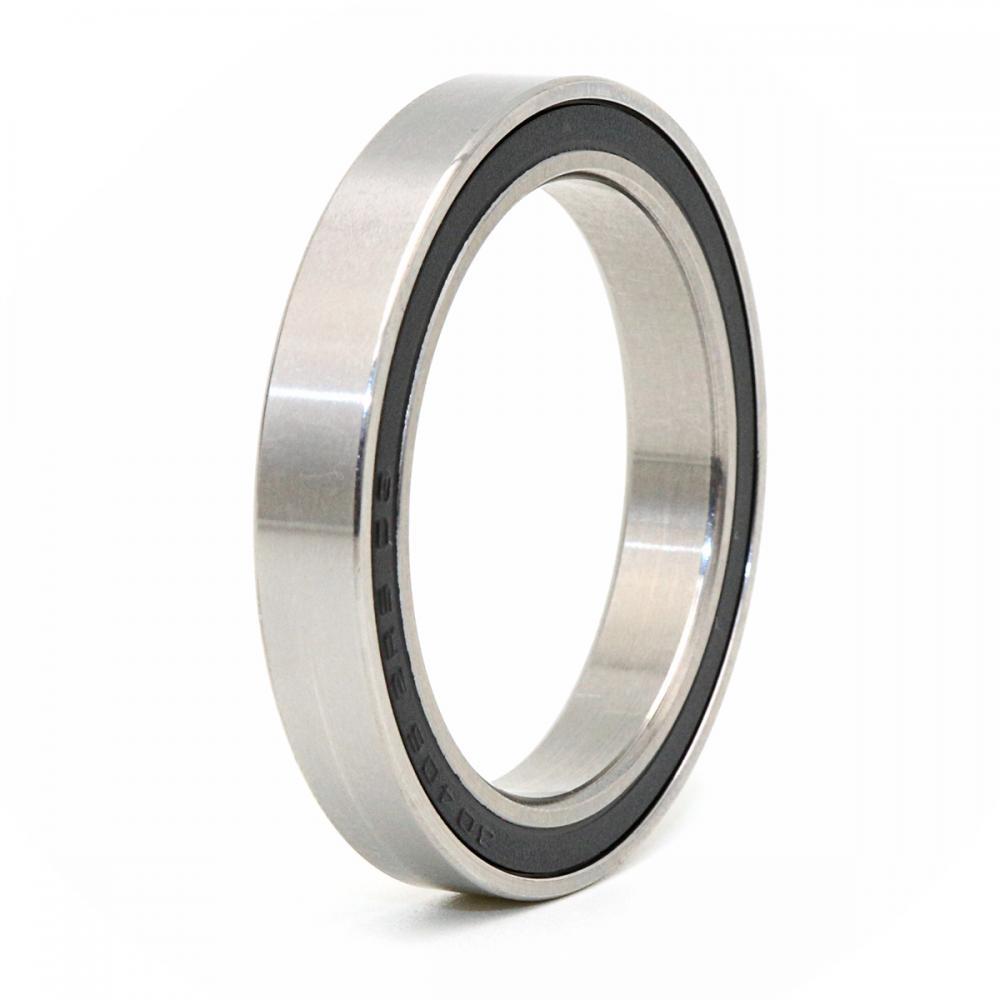
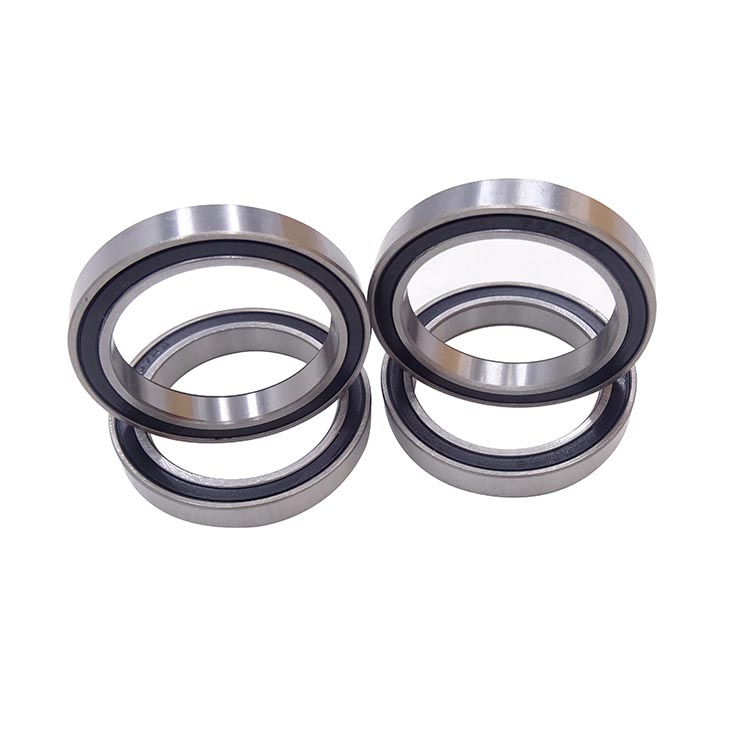
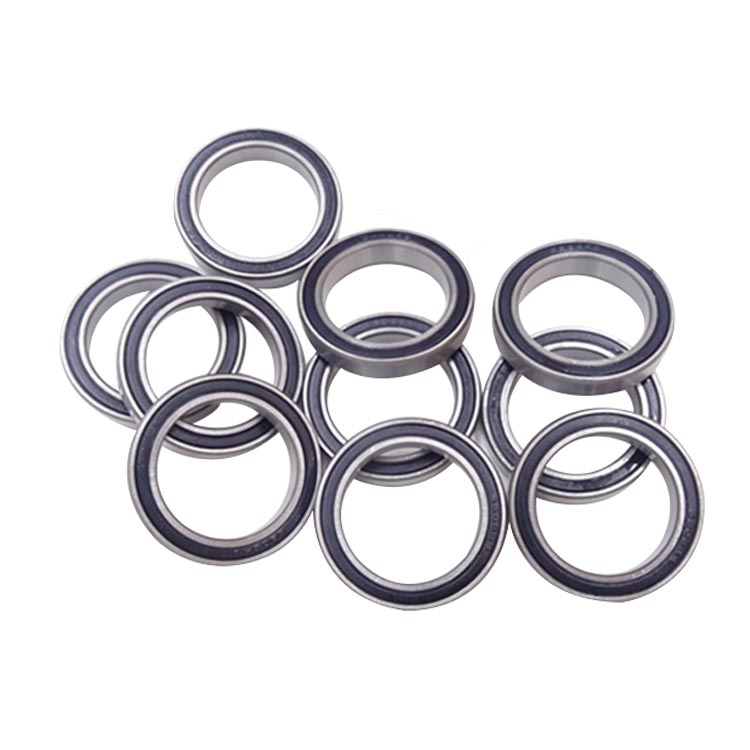




Thin wall ball bearings have a bearing inner diameter and outer diameter ratio less than a specified value. The ratio of bearing outer diameter to bearing inner diameter is 1.25 or less. It is called thin wall ball bearings, which means that the outer diameter-inner diameter value of the bearing is very small and the bearing wall is very thin.
The precision required by thin wall ball bearings is very high, because the wall is very thin, so the weight it can carry is also very low, and the impact resistance is very poor, so this must be selected according to the use environment!
Characteristics
The specific use of thin wall ball bearings:
Model airplanes, remote control cars, machine tools, motors, water pumps, agricultural machinery, textile machinery, laser printers, instruments, measuring instruments, electronic accessories, motors, motors, etc.




Welcome to contact me to get the price of thin wall ball bearings!
Thin Wall Ball Bearing,Thin Section Bearings,Thin Ball Bearing,Thin Wall Bearing
Shijiazhuang Longshu Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.longsbearing.com