Xinjiang is an important oil and gas production base in China. In 2013, it produced more than 50 million tons of oil and natural gas (oil and gas equivalents). It is expected that Xinjiang's oil and gas production will account for one-third of China's onshore oil production in the next decade. Xinjiang is arid-semi-arid region, with scarce water resources and fragile eco-environment. Most of the oil and gas resources are distributed in vast, dry and desert waters. The efficient use of water resources and ecological and environmental protection are more important and urgent than those of other oil fields.
The wastewater generated from the development of oil fields mainly includes the wastewater from separation of oil and water from production fluids, and downhole wastewater. After years of efforts, the wastewater treatment rate of crude oil produced from various oil fields in Xinjiang has reached 95%, and the reuse rate (mainly used for reinjection of formation pressurization) has reached more than 90%. The current pressing issue is the disposal of operational wastewater. Operational wastewater is the collective name for wastewater generated from downhole production operations such as oil fracturing, acidification, profile control, and water shutoff. Due to the high polymer content, various types of chemical additives, and heavy crude oil, the water quality is extremely complex, so far there is no ideal and Mature, low-cost treatment technologies have been stored in evaporation ponds for many years and reduced by evaporation.
With the continuous expansion of oilfield production capacity, the number of evaporation ponds has continuously increased and the impact on the environment has become increasingly prominent. Operational wastewater has become a potential source of pollution and potential safety hazards for various oilfields and is highly concerned by oilfields and local environmental protection agencies. In recent years, major domestic oilfields have carried out research and development related to operational wastewater treatment technologies, but they are still in the experimental stage of complicated process flow, low flow treatment, and high unit cost.
Commissioned by PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Branch, with the support of the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Western Action Plan, the research team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography Wei Guoguo, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Suzhou Nanotechnology and Nanobionics Institute, Xinjiang The Oilfield Company’s Engineering Technology Research Institute and other units systematically developed the Xinjiang oilfield operation wastewater treatment technology and equipment. After breakthroughs and breakthroughs, significant breakthroughs have been made and engineering applications have been realized.
The research team proposed and determined the technological route of "catalytic oxidation-reaction adsorption-gas flotation separation-deep filtration" and developed a highly targeted cationic and anionic water-dispersed polyacrylamide special agent. Integrated ozone and electrochemical synergistic reaction devices, internal recirculation tank and tubular reactors, radial flow air flotation machines, as well as special filtration materials for deep-filtered modified clay materials capable of removing soluble polymers, etc. The equipment has been continuously optimized and integrated to form a complete set of equipment for wastewater treatment in oilfield operations. The maximum processing capacity has reached 60m3/h.
Compared with the conventional flocculation sedimentation treatment process of the produced oil from the oilfield, the volume of equipment with the same treatment capacity of the whole set of equipment is reduced by 1/3, the reaction speed and efficiency are greatly improved, and the mixing reaction time of the additive is increased from the conventional 3-5 minutes. By 15-60 seconds, the processing efficiency increased by more than one time, and the processing capacity increased by more than 50%. Comparing with the domestically-developed five-step process for fracturing operation of oil and gas wells, and the four-step process for treating the backflow of oil and gas wells, the developed unit has high processing efficiency, applicability and stability. And the operability is strong, the complete treatment cost of the operation wastewater is reduced from 25 yuan/m3 to 12 yuan/m3. Related technologies have applied for 12 patents and 6 have been authorized (including 3 invention patents).
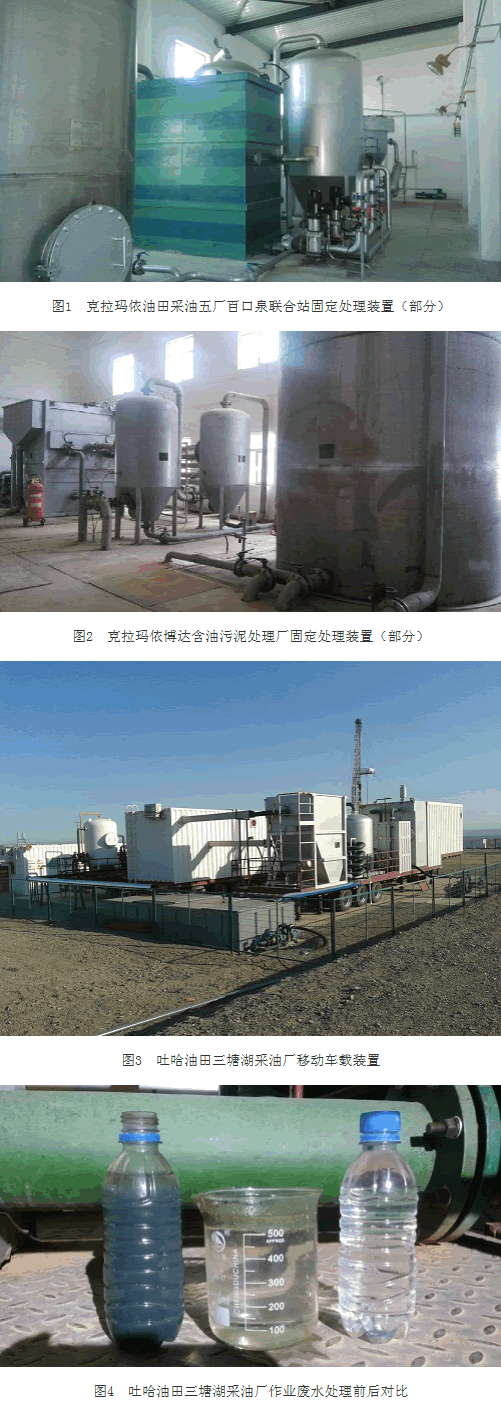
At present, three sets of processing units have been applied in Xinjiang Oilfield and the sales revenue is about 18 million yuan. From the end of 2013 to the beginning of 2014, completed the installation, commissioning and application of a complete set of processing equipment for wastewater treatment with a processing capacity of 60m3 per hour at Baikouquan Joint Station of the Karamay Oilfield No. 5 Plant (Fig. 1); Karamay Boda Oily Sludge Treatment Plant Complete sets of fixtures with processing capacity of 30m3 per hour (Figure 2), installation and commissioning completed in June 2014, formal commissioning in mid-September, and mobile vehicle-mounted devices of 30m3 per hour capacity (Figure 3), in 2014 8 The installation and commissioning of the oil production plant at the Santang Lake Oil Production Plant in the Tuha Oilfield was completed and put into production. So far, these three devices have handled more than 500,000 m3 of all types of wastewater, and all treated wastewater has reached the oilfield (Figure 4). This saves more than 30 million yuan for the company's saving of clean water and slow-down waste pools.
The above-mentioned oilfield operation wastewater treatment technologies and equipment in Xinjiang solve the problem of mixed waste liquid treatment and re-injection caused by well operations such as fracturing, acidification, profile control, and water shutoff in the oil field, and show high efficiency, low cost, and use in engineering applications. Convenient and comprehensive economic benefits have been highly recognized and recognized by the Xinjiang Oilfield Company and are planned to be applied in the oil production plants under its jurisdiction. After approaching, Tarim Oilfield, Qinghai Oilfield, Daqing Oilfield, and CNPC Kazakhstan Oilfield expressed their initial intention to adopt the technology and equipment researched and developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and related technologies and equipment showed good market prospects.
Although the operation technology and equipment for the operation of wastewater from Xinjiang oil fields have been applied in engineering applications, it is necessary to further improve the equipment classification and standardization design to form a series of models. At the same time, it is necessary to further develop special treatment agents to improve treatment efficiency and reduce costs in accordance with the water quality of the operation wastewater.
Dense oil fields and shale gas are new hotspots in energy development today. The large number of fracturing and returning fluids produced by the hydraulic fracturing technology will become a major environmental hazard. The research team is collaborating with the Xinjiang Oilfield Exploration and Development Company and the Engineering Technology Research Institute, etc., and is conducting a research on the technology and equipment for the treatment of fracturing and returning fluids in tight oil fields, with a view to revising the Changji tight oilfield (estimated reserves of one billion tons) in Xinjiang. The utilization of drainage resources provides technical support.
Sling,Flat Belt Sling,Webbing Sling Belt,Polyester Flat Webbing Sling
Jiangsu Zhongyi Work Rigging Co., Ltd. , https://www.zy-rigging.com