First, the concept of surface treatment
A process that uses the new edge technology of modern physics, chemistry, metallurgy, and heat treatment to change the condition and properties of the surface of a part to optimize its combination with the core material to achieve the desired performance, called surface treatment.
Second, the classification of surface treatment technology
1) Surface modification technology (metal, non-metal)
Through physical, chemical and other methods, the surface morphology, phase composition, microstructure, defect state and stress state of the material surface are changed. The chemical composition of the surface of the material is unchanged.
2) Surface alloying technology (metal)
The added material enters the substrate by a physical method to form an alloyed layer.
3) Surface conversion film technology (metal)
The additive material is chemically reacted with the substrate by a chemical method to form a conversion film.
4) Surface coating (plating) layer technology (metal, non-metal)
The additive material is plated and coated on the surface of the substrate by physical or chemical methods. The substrate does not participate in the formation of the coating.
Third, common surface treatment methods
3.1 Surface modification technology
Through physical, chemical and other methods, the surface morphology, phase composition, microstructure, defect state and stress state of the material surface are changed. The chemical composition of the surface of the material is unchanged.
3.1.1 Surface hardening
Surface hardening refers to a heat treatment method in which the surface layer is austenitized and rapidly cooled (quenched) by rapid heating without changing the chemical composition and core structure of the steel to harden the surface.
3.1.2 Sandblasting
Sand blasting is a process that uses high-speed jetting of sand or iron particles to impact the surface of the workpiece to improve the mechanical properties of the part and change the surface state.
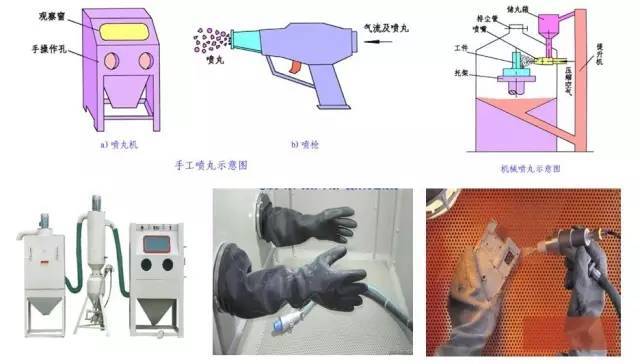
Sandblasting and shot peening, the process is similar, the main difference is in the diameter of the sand. The process is mainly used to improve mechanical strength and wear resistance, fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance of parts, and can also be used for surface matting, descaling and eliminating residual stress of casting, forging and welding parts.

3.1.3 Knurling
Knurling is applied to the surface of a rotating workpiece by a hard roller or roller at room temperature, and moves along the busbar to plastically deform and harden the surface of the workpiece to obtain an accurate, smooth and reinforced surface, or a specific pattern. Processing process.

3.1.4 Drawing
A technical processing method in which a metal is forced to pass through a mold under an external force, a metal cross-sectional area is compressed, and a desired cross-sectional area shape and size is obtained is called a metal wire drawing process. A tool that changes its shape and size is called a wire drawing die. Drawing can be made into straight lines, chaotic lines, corrugations, threads, etc. according to the needs of decoration.
1) Straight line drawing
It refers to the processing of linear lines by mechanical friction on the metal surface.
2) chaotic drawing
It is a kind of irregular, no-grain matt silk thread obtained by moving the metal plate back and forth and left and right under the high-speed running copper wire brush. This processing requires a high surface area of ​​the metal sheet.
3) Ripple
Generally made on a brush or a wiper. Using the axial movement of the upper set of grinding rolls, the surface of the metal plate is ground to obtain a wave pattern.
4) Thread
It is to use a small motor with a circular felt on the shaft, fix it on the table, at an angle of about 60 degrees to the edge of the table, and make a carriage with a fixed metal plate and attach a piece to the carriage. Straight polyester film is used to limit thread progression. Using the rotation of the felt and the linear movement of the carriage, a thread of uniform width is spun on the surface of the metal sheet.

3.1.5 polishing
Polishing is a kind of finishing method for modifying the surface of parts. Generally, only smooth surface can be obtained, which can not improve or even maintain the original processing precision. With the pre-processing conditions, the Ra value after polishing can reach 1.6-0.008 mm. According to the realization principle, it can be divided into mechanical polishing and chemical polishing.
1) Mechanical polishing
Polishing is performed by rolling and micro-cutting the surface of the workpiece with a flexible polishing wheel rotating at a high speed and a very fine abrasive. The polishing wheel is laminated with layers of canvas, felt or leather for the polishing of larger parts.

2) Drum polishing and vibration polishing
The workpiece, the abrasive and the polishing liquid are loaded into the drum or the vibration box, the roller slowly rolls or the vibration box vibrates, the workpiece and the workpiece, the workpiece and the abrasive rub each other, and the chemical action of the polishing liquid removes the oil stain and the rust layer on the surface of the workpiece. , the peaks are removed to obtain a smooth surface. It is used for the polishing of small and large parts, which is more productive and polished than the former.
3) Biopolishing
Biopolishing is a finishing process that uses cellulase to improve the surface of cellulosic fibrous products to achieve long-lasting pilling resistance and increase fabric finish and softness. Bio-polishing removes the fine fibers that protrude from the surface of the yarn. These micro-fibers are removed without pilling, the color is brighter, and the surface hair is reduced to make the fabric smoother.

3.1.6 Laser surface strengthening
Laser surface strengthening is to use a focused laser beam to strike the surface of the steel, heating the extremely thin surface of the workpiece to a temperature above the phase transition temperature or melting point in a very short time, and cooling the surface of the workpiece in a very short time. strengthen. Laser surface strengthening can be divided into laser phase transformation strengthening treatment, laser surface alloying treatment and laser cladding treatment.
The laser surface strengthening has small heat-affected zone, small deformation and convenient operation. It is mainly used for locally strengthened parts such as blanking die, crankshaft, cam, camshaft, spline shaft, precision instrument guide rail, high speed steel cutter, gear and internal combustion engine. Cylinder liners, etc.

3.2 Surface alloying technology
The added material enters the substrate by a physical method to form an alloyed layer. The typical process of this technology is the carburizing and nitriding treatment of metals. Usually, the metal and the osmotic agent are placed in a closed cavity, and the metal surface is activated by heating, vacuum, etc., and the carbon and nitrogen enter the metal matrix through decomposition, absorption, and diffusion processes.
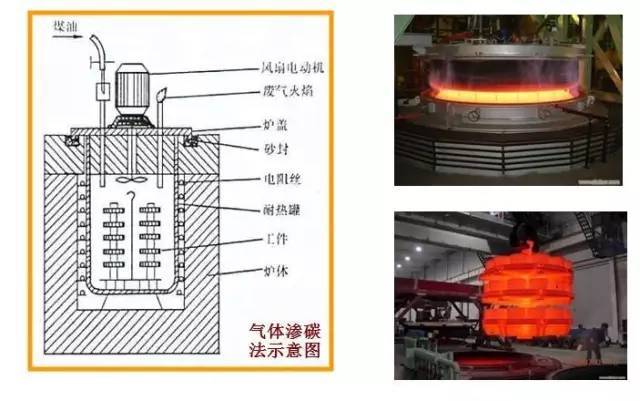
After the kerosene is dropped into the carburizing furnace, it undergoes high temperature thermal cracking to decompose carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), oxygen (O2), hydrogen (H2) and saturated hydrocarbons (CnH2n+2) and unsaturated hydrocarbons ( CnH2n) and other mixed gases.
Gas carburizing mainly utilizes carbon monoxide, saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and these gases are decomposed at the carburizing temperature to obtain carbon in the atomic state to produce carburization.
When carbon monoxide is carburized at high temperature, its decomposition rate is slow, and the decomposition and absorption are basically balanced. Therefore, there is generally no excess carbon deposition, and unsaturated hydrocarbons, which will precipitate carbon violently at the beginning of carburization to form a layer of carbon black. Attached to the surface of the part to prevent carburization. Therefore, the content of unsaturated hydrocarbons in the carburizing gas should be controlled to be lower.
3.3 Blackening and phosphating of steel
Blackening: It is a common method for metal heat treatment. The principle is to produce an oxide film on the metal surface to isolate the air and achieve the purpose of rust prevention. Blackening treatment can be used when the appearance requirements are not high, and the surface of the steel parts is blackened, and it is also called blue. Blue treatment is a chemical surface treatment. Its main function is to form a dense oxide film on the surface of the workpiece to prevent corrosion of the workpiece and improve the wear resistance of the workpiece. It is only a surface treatment and does not affect the internal structure. It has any effect, it is not heat treatment, and there is a fundamental difference between quenching.

Phosphating: It is a chemical and electrochemical reaction to form a phosphate chemical conversion film. The phosphate conversion film formed is called a phosphate film. The purpose of phosphating is mainly to provide protection to the base metal, to prevent the metal from being corroded to a certain extent; to base the paint before painting, to improve the adhesion and corrosion resistance of the paint layer; to reduce friction in the metal cold working process Lubrication is used. Phosphating is a commonly used pretreatment technology. In principle, it should be treated by chemical conversion membranes. It is mainly used for phosphating of steel surfaces. Phosphorification can also be applied to non-ferrous metals (such as aluminum and zinc). The process of immersing a workpiece (steel or aluminum, zinc) in a phosphating solution (some acid phosphate-based solution) and depositing a layer of water-insoluble crystalline phosphate conversion film on the surface, called phosphating .

Ball Valves,Flange Type Ball Valve,Flanged Ball Valve,Platform Flanged Ball Valve
ZHITONG PIPE VALVE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.ztongvalve.com