Abstract From 2009 to 2012, Europe was in deep debt crisis, but the German economy was outstanding and still strong. The driving force for German economic growth comes from its international industry, the international competitiveness maintained by its manufacturing industry. For Germany, manufacturing is...
From 2009 to 2012, Europe was in deep debt crisis, but the German economy was outstanding and still strong. The driving force for German economic growth comes from its international industry, the international competitiveness maintained by its manufacturing industry. For Germany, manufacturing is a traditional driving force for economic growth. The development of manufacturing is an indispensable factor for German industrial growth. Based on this consensus, the German government is pushing for further technological innovation. The key word is “Industry 4.0â€. ". Industry 4.0 is considered the fourth industrial revolution in Germany and is a strategy in the High-Tech Strategy 2020 published by the German government in November 2011 to support the development and innovation of a new generation of revolutionary technologies in the industrial sector. Germany's international competitiveness.
In April 2013, the German Machinery and Manufacturers Association, the German Information Technology, Communications and New Media Association, and the German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers Association established the “Industry 4.0 Platform†and submitted the final report of the Platform Working Group to the German government – - "Protecting the future of German manufacturing - recommendations for the implementation of the Industry 4.0 strategy." The report suggests that Germany's transition to Industry 4.0 requires a dual strategy, namely that Germany is to become a leading supplier of smart manufacturing technology and a leading market for CPS (Information Physics System) technologies and products. The report also looks ahead to the development prospects of the German Industry 4.0 strategy.
Industry 4.0 Evolution
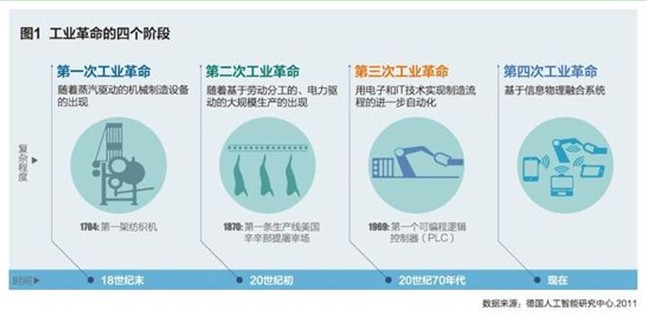
Industrial Revolution 1.0: The first industrial revolution began in Britain at the end of the 18th century and ended in the mid-19th century. The result of this industrial revolution is that mechanical production has replaced manual labor. The economic society has shifted from agriculture and handicrafts to a model of industrial and mechanical manufacturing that drives economic development.
Industrial Revolution 2.0: The second major change in the industrial field took place in the early 20th century, forming the stage of production line production. Through the successful separation of parts production and product assembly, a new model for mass production of products has been created. After the 1970s, as electronic engineering and information technology were enriched into industrial processes, production optimization and automation were achieved.
Industrial Revolution 3.0: The third industrial revolution began with a high degree of automation of the production process that took place during the second industrial revolution. Since then, machinery has been able to gradually replace human work.
Industrial Revolution 4.0: In the next 10 years, the fourth industrial revolution will enter a new era of “decentralized†production. Industry 4.0 achieves real-time management by determining network technologies such as manufacturing processes.
Industry 4.0 is essentially based on the "information physics system" to achieve "smart factory"
Industry 4.0 is actually the realization of "smart factory." The first industrial revolution began in the second half of the 18th century by the steam engine to achieve the mechanization of the factory; the second industrial revolution began in the second half of the 19th century with electricity to achieve large-scale mass production; the third industrial revolution began in the second half of the 20th century Automation of manufacturing through electrical and information technology.
Industry 4.0 will evolve further on the basis of the first three industrial revolutions, implementing new manufacturing methods based on the Cyber ​​Physical System. Information physics system refers to the close connection of the real world through the sensor network, and the advanced computing power of cyberspace is effectively applied to the real world. In the manufacturing process, all data related to design, development and production will be collected by sensors. Analyze to form an intelligent production system that can operate autonomously.
Industry 4.0 core is a dynamically configured production method
The dynamically configured production method described in the Industry 4.0 report mainly refers to the robot (workstation) engaged in the operation, which can access all relevant information in real time through the network, and independently switch production methods and replace production materials according to the information content, thereby adjusting to become the most matching mode. Production operations. The dynamically configured production method enables different designs, component components, product orders, production plans, manufacturing, and logistics to be delivered to each customer and product, eliminating waste in the entire chain. Unlike traditional production methods, dynamically configured production methods can change the original design at any time before or during production.
For example, current car production is mainly a production line production method in accordance with a pre-designed process. Although there are some mixed-flow production methods, the production process must be carried out on a production line composed of many machines, so that product design diversification will not be achieved. The MES (Manufacturing Execution Management System) that manages these production lines should have brought more flexibility to the production line, but it is not limited by the hardware constraints of many machines that make up the production line.
At the same time, the workers operating on different production lines are distributed in various workshops, and they will not master the entire production process, so they can only play a role in a fixed work. As a result, it is difficult to meet the needs of customers in real time.
In the smart factory depicted in Industry 4.0, the concept of a fixed production line has disappeared, and a modular production method that can be dynamically and organically reconfigured has been adopted.
For example, a production module can be viewed as an "information physics system" in which an automobile being assembled can self-discipline shuttle between production modules to accept the required assembly work. Among them, if bottlenecks occur in the production and parts supply links, the production resources or parts of other models can be dispatched in time to continue production. That is to choose the appropriate production module for each model self-discipline, and carry out dynamic assembly work. In this dynamically configured production mode, the original comprehensive management function of the MES can be exerted, and the entire production process such as design, assembly, and testing can be dynamically managed, which not only ensures the operational efficiency of the production equipment, but also diversifies the production types. .
Industry 4.0's primary goal is factory standardization
One aspect of German industrial influence is “standardizationâ€. The international standard IEC 61131-3 (PLCopen) of the PLC programming language is mainly from German companies; CAN, Profibus and EtherCAT, which are popular in the field of communication, were also born in Germany.
The Industry 4.0 Working Group believes that the implementation of Industry 4.0 requires action in eight key areas. The first area is the "standardization and reference architecture." The standardization work mainly focuses on the cooperation mechanism in each link of the smart factory ecological chain to determine what information can be exchanged. To this end, Industry 4.0 will develop a common set of standards to make the cooperation mechanism possible and optimize the production process through a range of standards such as cost, availability and resource consumption.
In the past, most of what we heard was “standardization of productsâ€, while German Industry 4.0 will promote “standardization of factoriesâ€, promote the manufacturing production model to the international market by standardization of smart factories, and standardize and improve technological innovation and model innovation. Market-oriented efficiency continues to maintain the world leading position of German industry.
At present, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other ministries are also drawing on the German experience to compile "Made in China 2025" and strive to promote China to become an industrial power. The author believes that German Industry 4.0 has received unprecedented attention, but how to learn from the standardization issues in Industry 4.0, especially Industry 4.0, deserves our deep thinking.
Other Camping Light,Rechargeable Lantern,Led Kerosene Lamp,Tent Camping Lantern
NINGBO ZHENGUO INTELLINGENT LIGHTING CO.,LTD , https://www.zguolight.com