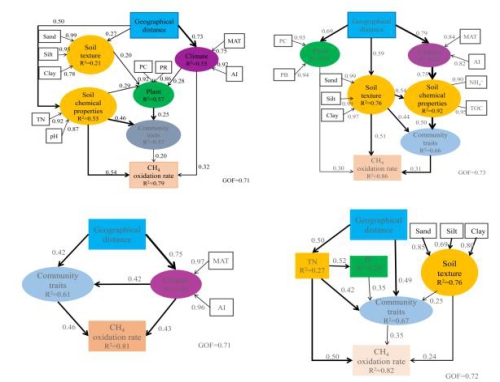
Path Models Affecting Soil Methane Oxidation Potential at Different Sub-regional and Regional Scales
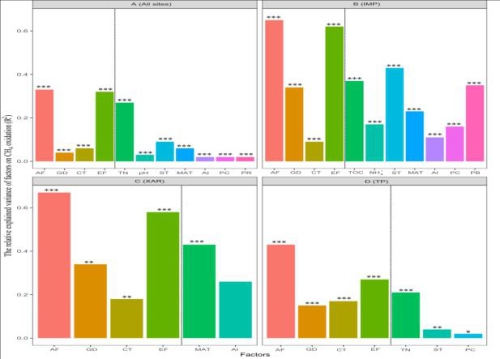
Key environmental factors affecting methane oxidation potential at different subregional and regional scales
Methane is the greenhouse gas that is second only to carbon dioxide emissions. Its greenhouse effect is 28 times that of carbon dioxide. Oxidation of methane by methane-oxidizing bacteria in dryland soils is an important biological sink for atmospheric methane. Previous studies have shown that climate, vegetation, soil physical and chemical properties, and community distribution of methane oxidizing bacteria all affect soil methane oxidation, but the main factors affecting the oxidation potential of methane in different regions are unclear.
Dr. Yong-Ping Ping from the Li Xiangzhen Research Team of the Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, studied the influencing factors of methane oxidation potential in grassland soils in Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and in three different subregions (Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, and Tibetan Plateau) and regional scales. On the basis of a comprehensive analysis of the geographical distance, environmental factors (climate, vegetation, and soil physical and chemical properties) and the relative contributions of methane oxidizing bacteria community distribution to methane oxidation potential, the key factors affecting soil methane oxidation potential at different sub-regional and regional scales were identified. And analyze its impact mechanism. The results show that the environmental factors have the highest degree of explanation for the oxidation potential of methane compared to geographical distances, but the key environmental factors affecting the oxidation potential of methane have a scale dependence. Soil total nitrogen is a key environmental factor affecting the oxidation potential of methane over the entire regional scale. It can affect the methane oxidation potential of the soil by affecting the plant growth and the community distribution of methane oxidizing bacteria; it affects the Inner Mongolia grassland at different sub-regional scales. The key environmental factors of soil methane oxidation potential are soil organic carbon and soil texture. The key environmental factors affecting soil methane oxidation potential in Xinjiang are aridity degree and average annual temperature; the key environment affecting methane oxidation potential of grassland soil in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The factor is total soil nitrogen. The results of the study will help scientists to predict and understand the response of methane oxidation potential in different regions to global climate change.
The study was funded by the Strategic Pilot Science and Technology Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the China Biodiversity Monitoring Network (Sino BON). The article was published on Soil Biology & Biochemistry.
It can be equipped with a scrolling display that displays 300-500 words of display content. It can also be equipped with intelligent infrared probe anti-collision device, which can automatically return to work when people or foreign objects are 20-30CM, thus ensuring the safety of vehicles and pedestrians.It can automatically open and close when automatic clutch is cut off. Manually open and close when manual clutch is cut off. The control system has control panel, push button switch, and other requirements. Equipped with wireless remote control.The door body is made of high-quality stainless steel and aluminum alloy profiles, and is hinged by the parallelogram principle. The drive is driven by special motor, worm and worm gear deceleration, and has automatic clutch or manual clutch.
Factory Sliding Retractable Gate,Aluminum Alloy School Sliding Gate,Automatic Electric Single Double Gate,Store Retractable Gate
Shenzhen Hongfa Automatic Door Co., Ltd. , https://www.hfautodoors.com