In chemical engineering and other engineering technologies, electromagnetic flowmeters are commonly used to measure the flow of pipeline liquids, and the influence of excitation methods on meter accuracy, power consumption, and noise is becoming more and more obvious.
What are the excitation methods of electromagnetic flowmeters?
In chemical engineering and other engineering technologies, electromagnetic flowmeters are commonly used to measure the flow of pipeline liquids, and the influence of excitation methods on meter accuracy, power consumption, and noise is becoming more and more obvious. For the selection of the excitation method, the main use at home and abroad is constant square wave excitation. Based on the analysis and comparison of various excitation methods, this paper focuses on the square wave magnetic field method to suppress noise and improve the accuracy, and proposes an improved scheme for the excitation waveform to reduce power consumption.
1 excitation method analysis
The electromagnetic flowmeter is a meter that measures the volumetric flow rate of a conductive liquid according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which induces an electromotive force U and a flow rate L. And the relationship of the flow rate Q can be expressed by the following formula
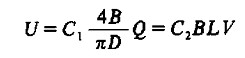
(1)
Where: B is the magnitude of the magnetic induction; c1, c2 are the conversion coefficients; D is the inner diameter of the measuring tube; L is the length of the conductor in the direction of the vertical cutting magnetic field in the magnetic field.
It can be seen that the induced electromotive force u is linear with the flow velocity V or the liquid volume flow rate Q, and is independent of the density, viscosity, temperature, pressure and other characteristics of the measured conductive medium. This is a major feature of electromagnetic flowmeters.
DC excitation, that is, a magnetic field is a constant magnetic field generated by a direct current or permanent magnet. The advantage of this DC magnetic field transmitter is that the excitation method is simple and there is no noise inherent in the alternating magnetic field transmitter. However, DC excitation will cause polarization of the electrolyte liquid in the measuring tube, which seriously affects the accuracy of the meter. When measuring liquid metals that have high conductivity and cannot be electrolyzed, such as mercury at normal temperature, high-temperature sodium, helium, etc., it is advantageous to use a DC magnetic field transmitter.
Power frequency AC excitation is used more in early electromagnetic flowmeters. Its main advantage is that it can eliminate the polarization of the electrode surface, and the excitation circuit is simple. In addition, with AC excitation, the output signal is also AC, and it is much easier to amplify and convert the low-level AC signal than the DC signal. However, the amplitude stability and frequency stability of this method are poor. Moreover, due to the high frequency, the in-phase noise generated by the eddy current is also large, and the differential noise compensation is difficult, and it is not used much at present. In addition, the use of commercial power as the excitation current is susceptible to grid voltage and frequency fluctuations, so necessary compensation measures are necessary.
The main purpose of dual-frequency excitation is to make the electromagnetic flowmeter respond quickly to flow changes, zero stability and insensitivity to flow noise. The main principle is to use the zero-stability characteristics of the lower excitation frequency and the fast dynamic response characteristics of the higher excitation frequency. The performance of the two complement each other to improve the dynamic response and zero stability of the electromagnetic flowmeter.
2 constant square wave excitation
2.1 Constant voltage square wave excitation
This is one of the commonly used excitation methods for electromagnetic flowmeters. This method is widely used in electromagnetic flowmeters produced at home and abroad. It has a simple circuit and is sampled at steady state. At this time, the influence of differential noise is small and negligible. Select a lower excitation frequency to maintain zero stability. Proper selection of rest time can reduce excitation power consumption.
But it also has its own shortcomings. Assuming that the voltage source is a step signal, T>>f in the design, then
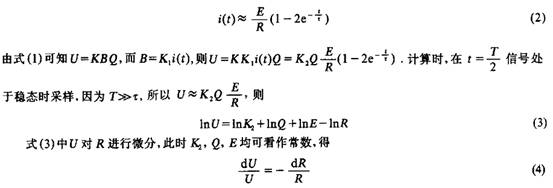
For copper resistance, R = R. [1+a(T_T0). Where: i(t) is the signal current; E is the voltage source amplitude; R is the copper resistance value; T is the time constant; K, K1, K2 are the transformation coefficients; T is the excitation signal period; a is the copper resistance temperature coefficient a =3.93×10-3/°C.
If the ambient temperature changes by 20 ° C, then -dU / U - = - a ΔT - = 7.86%. Obviously, this has a great influence on the signal. It can be seen that in the constant voltage square wave excitation, the temperature stability is very poor.
2.2 constant current square wave excitation
Constant current square wave excitation has all the advantages of constant voltage square wave excitation, and the effect of constant temperature source can eliminate the bad influence of copper resistance temperature characteristics. B=K1i(t)= K1I, U=KBQ=K K1IQ=CQ. Where: C is the transform coefficient; I is the constant current source amplitude.
This type of excitation not only overcomes the shortcomings of DC and AC excitation, but also solves the interchangeability problem between transmitter and converter, and should be widely used.
3 A solution to reduce excitation power consumption
Rectangular wave excitation is generally used at home and abroad. However, a large pressure drop will occur on the constant current source. Increase power consumption. In some explosion-proof, battery-powered electromagnetic flowmeters, this approach can cause problems. The waveform can be improved to reduce the excitation power consumption.
Currently, there is an excitation waveform shown in Figure 1. In order to reduce the excitation power, this paper attempts the intermittent waveform shown in Figure 2.
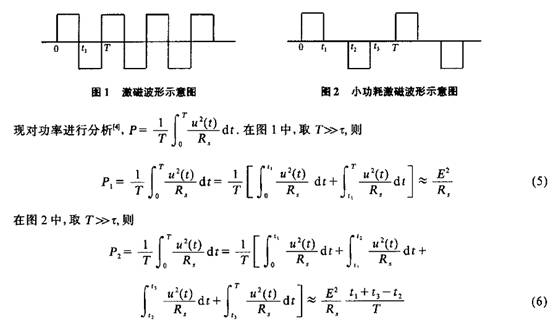
Where: RS is the equivalent resistance of the excitation coil.
Comparing equations (5) and (6), it can be seen that Pl>P2, that is, the intermittent waveform has lower power consumption. Therefore, the appropriate selection of t1, t2, t3 size can effectively reduce the excitation power consumption.
4 Conclusion
The constant current intermittent square wave excitation not only suppresses the noise, but also improves the accuracy of the electromagnetic flow meter and reduces the power consumption. However, it is not perfect in terms of zero characteristics and dynamic response, and can be combined with double-excitation to improve its performance. Therefore, fully improving the comprehensive performance index is the development trend of electromagnetic flowmeter technology. Orifice flowmeter http://
Magnetic flap level gauge http://
Input level transmitter http://
Turbine flow meter http://
Http://news.chinawj.com.cn
 Editor: (Hardware Business Network Information Center) http://news.chinawj.com.cn
Editor: (Hardware Business Network Information Center) http://news.chinawj.com.cn 
Floor drain
Floor drain is a plumbing fixture that is installed in the floor of a structure, mainly designed to remove any standing water near it. They are usually round, but can be also square or rectangular. Our floor drain`s size has 4", 6", in diameter. They are made of metal, like brass, stainless steel. Floor drains can also be found in commercial basements, restrooms, kitchens, refrigerator areas, shower room, laundry facilities and near swimming pool etc.
Brass Floor Drain,Stainless Steel Floor Drain,Floor Drain Strainer,Square Floor Drain
SHENZHEN KING OF SUN INDUSTRY CO.,LTD , https://www.handybasinfaucet.com