 |
Fig.1 Distribution of crops sown area and straw yield in 31 provinces and cities in China
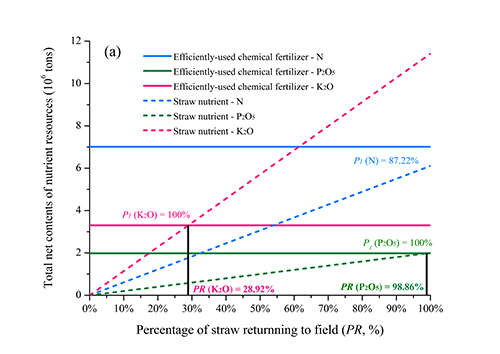
Fig.2 Alternative contribution of straw nutrient resources to nitrogen (N), phosphate (P2O5) and potash (K2O) under different returning ratios
As one of the largest agricultural countries in the world, China has abundant straw resources. Currently, China's crop straw is mainly used for bioenergy, livestock feed, and farmland fertilizers. At the same time, China is also a big country in the production and use of chemical fertilizers, and chemical fertilizers contribute a lot to increasing grain production. In 2017, the Ministry of Agriculture issued the “13th Five-Year Plan for Agricultural Science and Technology Development†notice, stating that the comprehensive utilization rate of crop stalks reached more than 85% during the 13th Five-Year Plan period; in addition, the Ministry of Agriculture formulated the “use of chemical fertilizers by 2020. Zero Growth Action Plan, and strive to achieve zero growth of main crop fertilizer use by 2020. In the context of this policy, how to balance the relationship between straw return and chemical fertilizer application and how to ensure national food security under the precondition of improving soil quality has become a major challenge for the green development of China's agriculture in the new era.
The Liu Qing Group of the Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is based on the official statistical yearbook of China's official statistics and collected a total of the major crop yields, sown area, chemical fertilizer application, straw yield, straw from 31 to 2014 in China's 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government). Data on nutrient resources, etc., and for the first time quantitative assessment of the potential contribution of straw nutrient pool to chemical fertilizer substitution. The study found that there are a large number of nutrient pools in the straw. Considering the amount of chemical fertilizers that can be effectively used by plants, theoretically, 28.92% and 98.86% of straw returning rates can completely replace the effective application rates of potash and phosphate fertilizers. 100% Straw returning can replace 87.22% of the effective amount of nitrogen fertilizer. The results show that straw returning is one of the potentially important measures to achieve zero-growth fertilizer operations and maintain stable grain yields. To this end, researchers have advocated straw returning as the main method of straw resource utilization and preferential incentive policies. At the same time, they should vigorously support the new straw decomposition technology and develop more efficient returning strategies to ensure the sustainability of China's green agriculture. Develop and achieve the goal of zero growth of fertilizer use during the “13th Five-Year Plan†period.
The study was titled Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. It was published in the International Energy Review Journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. The team members Yin Huajun and Zhao Wenqiang were the co-first authors and Liu Qingwei was the author of the correspondence. .
Dry Oven,Laboratory Oven,Binder Oven,Vacuum Drying Oven
Zenith Lab (Jiangsu) Co.,Ltd , https://www.zenithlabo.com